The landscape of healthcare is rapidly evolving, and at the forefront of this transformation are two of the most groundbreaking advancements in modern technology: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotics. These technologies have begun to reshape medical practices, improve patient outcomes, enhance precision in treatment, and optimize healthcare operations. The application of AI and robotics is not just a passing trend but a pivotal part of the ongoing revolution in the medical field.
In this article, we will explore the role of artificial intelligence and robotics in medical innovations, examine their various applications, highlight real-world examples, and delve into the potential challenges and future prospects of these technologies in the healthcare sector.
Key Takeaways
- AI and Robotics Enhance Precision: These technologies improve diagnostic accuracy and surgical precision, leading to better patient outcomes.
- AI Supports Personalized Medicine: AI helps create tailored treatment plans based on individual patient data, increasing the efficacy of treatments.
- Robotics Revolutionize Surgery and Rehabilitation: Robots assist in minimally invasive surgeries and support patients in their rehabilitation.
- AI Streamlines Healthcare Administration: AI optimizes administrative tasks, reducing workloads for healthcare professionals and improving efficiency.
- Challenges Remain for Widespread Adoption: High costs, data privacy concerns, and regulatory hurdles must be addressed for AI and robotics to reach their full potential in healthcare.
The Intersection of AI and Robotics in Medicine
Artificial intelligence refers to the ability of machines and systems to mimic human cognitive functions like learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making. In medicine, AI can process vast amounts of medical data, identify patterns, and support decision-making in diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient monitoring.
Robotics, on the other hand, encompasses the use of machines or robotic systems to perform tasks that were previously done manually. In healthcare, robotics plays a significant role in surgery, rehabilitation, and patient care, offering greater precision and reducing human error.
When combined, AI and robotics offer an innovative synergy that brings together the computational power of AI with the dexterity, efficiency, and precision of robotics. Together, they promise to push the boundaries of what is possible in healthcare, from surgical procedures to administrative tasks, enhancing both clinical and operational outcomes.
How AI and Robotics Are Revolutionizing Healthcare
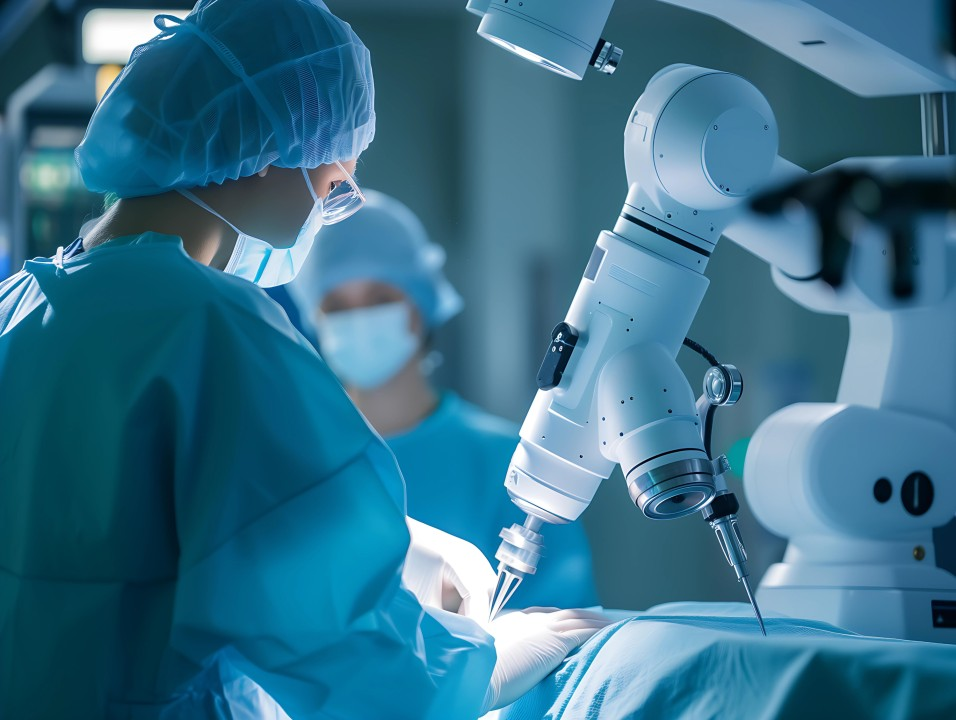
1. Enhancing Surgical Precision and Efficiency
- One of the most well-known applications of robotics in medicine is in the field of robotic surgery. Robotic surgery allows surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with high precision, flexibility, and control, often resulting in quicker recovery times for patients and fewer complications.
- Robots such as the da Vinci Surgical System are equipped with advanced AI capabilities that assist surgeons in performing complex operations with unprecedented precision. These robots can also filter out the “shaky hand” effect, allowing for smaller, more accurate incisions, which can lead to faster healing and minimal scarring.
- AI plays a critical role here by analyzing data from imaging systems and the robot’s sensors to provide real-time feedback to the surgeon. This enhances the decision-making process during surgery, ensuring that the right course of action is taken based on a thorough analysis of the patient’s condition.
2. AI-Driven Diagnostic Tools
- AI is transforming diagnostic processes by helping healthcare providers interpret medical data faster and more accurately. Machine learning algorithms, a subset of AI, are capable of analyzing vast datasets, including medical imaging, electronic health records (EHRs), and genetic data, to provide early diagnosis and identify potential risks in patients.
- One prime example is AI’s role in radiology. AI algorithms have been trained to interpret medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs with a high degree of accuracy. For example, Google Health’s AI tool for breast cancer detection showed promise in outperforming radiologists in detecting cancer. By analyzing patterns in mammograms, AI can identify abnormalities that may go unnoticed by the human eye, ensuring early intervention and saving lives.
- Moreover, AI-powered diagnostic tools are also being used to predict disease progression and suggest personalized treatment plans. For example, AI can analyze the genetic makeup of cancerous cells and predict how they will respond to specific treatments, helping oncologists choose the most effective approach for each patient.
3. Robotics in Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
- Robotics is playing an increasingly important role in rehabilitation and physical therapy, particularly for patients recovering from strokes, spinal injuries, or surgeries. Robotic exoskeletons and assistive devices are being used to help patients regain mobility and independence.
- Robotic rehabilitation devices are equipped with sensors that can adjust therapy sessions based on real-time data about a patient’s progress, enabling personalized care that adapts to the individual’s needs. For example, the Lokomat is a robotic system designed to help patients with mobility impairments walk again, providing a safe and controlled environment for therapy.
- AI is also being integrated into rehabilitation robotics to monitor patient progress and suggest adjustments to therapy based on real-time data, such as muscle response, movement, and endurance. This combination of robotics and AI ensures that rehabilitation therapy is more efficient, effective, and personalized.
4. AI in Drug Discovery and Personalized Medicine
- The process of drug discovery has traditionally been long, expensive, and fraught with uncertainty. However, AI has significantly accelerated the process by analyzing vast datasets and predicting how different compounds will interact with specific diseases. AI models can simulate how new drugs will behave in the human body, allowing researchers to identify promising compounds much faster than through traditional methods.
- Additionally, AI is helping create personalized treatment plans for patients based on their genetic makeup and unique health characteristics. Precision medicine leverages AI algorithms to analyze genomic data, lifestyle factors, and medical history to determine the most effective therapies for an individual, resulting in improved patient outcomes and minimized side effects.
5. Optimizing Healthcare Administration and Workflow

- AI is also being leveraged to streamline administrative tasks in healthcare settings. From scheduling appointments to processing insurance claims and managing patient data, AI can help reduce administrative burdens, allowing healthcare professionals to focus on patient care.
- AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are also becoming common in healthcare for answering patient inquiries, collecting medical histories, and even providing basic triage advice. This frees up time for healthcare providers, reduces wait times for patients, and helps improve overall service delivery.
- Robotics is also playing a role in administrative tasks. Robotic process automation (RPA) systems are being used to automate repetitive tasks such as data entry, billing, and compliance reporting, which increases efficiency and reduces human error in administrative functions.
Challenges in Implementing AI and Robotics in Healthcare
While AI and robotics hold enormous potential for transforming healthcare, their integration into the medical field is not without challenges.
1. Data Privacy and Security Concerns
The integration of AI and robotics in healthcare relies heavily on patient data, such as medical records, genetic information, and imaging. With the increased use of digital health tools, there are concerns about data privacy and security. Healthcare providers must ensure that they comply with data protection regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and implement robust cybersecurity measures to prevent breaches.
2. High Costs and Accessibility
AI and robotic systems often come with high upfront costs, which can be a barrier to their widespread adoption, especially in resource-limited settings. Smaller hospitals and clinics may struggle to invest in these technologies, limiting access to advanced treatments and care.
However, as technology continues to advance and become more cost-effective, we can expect wider adoption and more equitable access to these tools.
3. Ethical and Regulatory Concerns
The use of AI in decision-making raises ethical concerns about accountability and the potential for bias. AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on, and if that data is biased or incomplete, the resulting decisions could be flawed. Additionally, the regulatory environment around AI and robotics in healthcare is still evolving, and ensuring the safety and efficacy of these technologies requires clear regulatory frameworks.
4. Integration with Existing Healthcare Systems

Integrating AI and robotics into existing healthcare systems can be a complex and time-consuming process. Healthcare providers may face challenges in training staff, adapting workflows, and ensuring that new technologies align with existing infrastructure. Furthermore, these technologies require regular maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting, which adds to the complexity of integration.
The Future of AI and Robotics in Medicine
As we look to the future, the role of AI and robotics in medicine is set to expand even further. We can expect more sophisticated AI algorithms that provide even greater accuracy in diagnostics, personalized treatments, and predictive analytics. Robotics will continue to evolve, becoming more adaptable and capable of performing increasingly complex procedures with even greater precision.
In the coming years, we may see the rise of AI-powered robotic surgical assistants, capable of performing surgeries with little or no human intervention, guided by vast databases of medical knowledge. Similarly, we could see smart medical robots used in patient care, remotely assisting with tasks such as monitoring vital signs, administering medications, and even performing routine check-ups.
Moreover, as AI systems become more capable of understanding and mimicking human emotions, robotic companions could play a key role in providing care for elderly or chronically ill patients, offering not only physical assistance but also emotional support and companionship.
The Role of AI and Robotics in Enhancing Healthcare Accessibility
One of the most transformative aspects of AI and robotics in healthcare is their potential to democratize access to high-quality medical care, especially in underserved or rural areas where healthcare resources are scarce. These technologies have the ability to bridge the gap between patients and specialists, creating a more equitable healthcare system.
1. Remote Monitoring and Telemedicine
- Telemedicine has already become a powerful tool in providing remote consultations, especially for patients in remote areas. AI and robotics can take this one step further by enabling remote monitoring systems that track patient health in real-time. For example, AI algorithms can continuously analyze patient data, such as blood pressure, heart rate, and glucose levels, sent via wearable devices or sensors embedded in robotic systems. These tools can alert doctors to any concerning changes, allowing for immediate intervention even if the patient is miles away.
- Additionally, robotic telepresence allows doctors to virtually “visit” patients in remote locations. With the aid of AI, these robots can interact with patients, take vital signs, and even perform minor examinations, all while transmitting data to healthcare providers in real-time.
2. AI-Powered Chatbots for Patient Interaction
- AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are increasingly being used to engage with patients before they even step into a clinic. These AI systems can provide initial consultations by gathering medical histories, asking diagnostic questions, and even offering personalized health advice based on the input they receive. For example, IBM’s Watson Health can process natural language to understand patient queries, provide recommendations, and flag any urgent issues that require immediate attention.
- Chatbots powered by AI can also help reduce the burden on overworked healthcare professionals, as they can handle routine queries, reminders, and administrative tasks, leaving doctors more time for complex patient cases.
AI and Robotics for Early Detection of Diseases
Early disease detection is often the key to improving patient outcomes. AI and robotics are playing pivotal roles in detecting diseases at earlier stages than previously possible, significantly improving survival rates and reducing the overall burden on healthcare systems.
1. AI for Early Cancer Detection
AI has proven invaluable in the early detection of cancer, especially in radiology and pathology. By analyzing medical imaging data from X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, AI algorithms can detect abnormal growth patterns indicative of tumors that may be too small or subtle for human eyes to detect. Deep learning algorithms are particularly adept at identifying nuances in imaging data that correlate with early-stage cancers such as breast, lung, and skin cancer.
For example, researchers at Google Health have developed an AI tool that can detect breast cancer from mammograms with higher accuracy than radiologists. This technology can catch cases earlier, potentially saving lives and enabling more effective treatments.
2. AI for Alzheimer’s Disease and Neurological Conditions
In neurology, AI has been utilized to detect Alzheimer’s disease and other neurological conditions early in their progression. By analyzing brain scans, AI can identify early biomarkers that may indicate the onset of Alzheimer’s before symptoms become noticeable. Moreover, AI can track the progression of neurological diseases over time, allowing doctors to adjust treatment strategies accordingly.
The incorporation of AI in diagnosing Alzheimer’s can help doctors distinguish between normal age-related cognitive decline and early stages of dementia, leading to earlier interventions and better management of the disease.
3. Robotic Endoscopy and Diagnostics
Robotic endoscopy is another area where AI is enhancing early disease detection. Endoscopes—thin, flexible tubes with a camera attached—are commonly used for internal examinations to detect conditions like cancer, ulcers, and infections. AI-equipped robotic endoscopes can autonomously navigate through the body, capturing high-quality images and using real-time data to detect abnormalities. This process provides doctors with greater detail than traditional methods and ensures that no area is overlooked.
AI and Robotics in Surgery: Advanced Applications
While robotic surgery has already made a tremendous impact, the next stage of development promises even more advanced capabilities that go beyond the current state of robotic systems. Some of the most exciting prospects include autonomous surgery, AI-assisted surgery with enhanced human-robot collaboration, and advanced robotic surgical assistants.
1. Autonomous Surgical Robots
Autonomous surgery is one of the most ambitious goals of combining AI and robotics in medicine. This concept refers to the use of AI-powered robots capable of performing complex procedures with little or no human intervention. While we’re not yet at the stage where fully autonomous surgery is common, there have been significant strides made in the direction of robot-assisted surgeries, where AI provides real-time guidance to surgeons.
In the future, it’s conceivable that AI systems could not only assist but take on entire procedures, especially in less complex surgeries where human oversight might not be necessary. For example, in laparoscopic surgeries, robots can already perform some tasks autonomously under human supervision. However, advancements in AI algorithms and real-time decision-making capabilities will further enhance the robot’s ability to function autonomously, improving precision and reducing human error.
2. Human-Robot Collaboration in Surgery
Even if fully autonomous robots are a distant reality, human-robot collaboration is becoming a fundamental part of modern surgical practice. In robot-assisted surgeries, AI tools can assist the surgeon in making real-time decisions during operations. The da Vinci Surgical System, for example, allows surgeons to control robotic arms that perform highly detailed and delicate tasks. AI algorithms provide feedback based on data collected during surgery, such as patient vitals, anatomical structures, and real-time conditions.
This symbiotic relationship between AI, robotics, and surgeons can reduce risks, improve accuracy, and ultimately lead to faster patient recovery.
3. AI-Enabled Surgical Training and Simulation

AI-powered simulators are now being used to train surgeons. These simulators, combined with robotics, can create highly realistic virtual environments that replicate actual surgeries. Through machine learning, these simulators learn from the experiences of real-world surgeries, refining their ability to mimic surgical conditions. Trainees can use these systems to perform virtual surgeries that mimic real-life scenarios, improving their skills before they perform procedures on actual patients.
Challenges in Scaling AI and Robotics in Healthcare
Despite the tremendous promise that AI and robotics hold for healthcare, there are several key challenges that must be addressed in order to scale these technologies effectively.
1. Regulatory and Ethical Issues
As with any new technology, AI and robotics face significant regulatory hurdles before they can be widely adopted in medical practice. These technologies must meet stringent standards for safety, efficacy, and patient privacy. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) must establish clear guidelines for the approval and oversight of AI and robotic devices in healthcare.
Additionally, AI systems must be free of bias, as algorithms trained on biased data could lead to unequal care or incorrect diagnoses. Transparency in AI decision-making processes is critical to ensuring accountability and ethical use of these technologies.
2. High Costs and Financial Barriers
AI and robotic systems are often expensive, which presents a financial challenge for healthcare facilities, especially in low-resource settings. The initial investment in AI algorithms, robotics infrastructure, and training is substantial, and not all institutions can afford these technologies. Overcoming this barrier will require cost reduction strategies and more widespread adoption to make AI and robotics accessible to all healthcare providers.
3. Data Privacy and Security Concerns
AI and robotic systems depend on large datasets, including sensitive patient information. With the rise of telemedicine, remote monitoring, and connected devices, ensuring the security and privacy of patient data is critical. Cybersecurity threats, such as data breaches, must be mitigated to protect patient confidentiality and prevent malicious attacks on medical devices.
The Future Outlook for AI and Robotics in Healthcare
- The future of AI and robotics in medicine is bright, with possibilities that continue to expand. By 2030, it’s expected that AI will become integral to precision medicine, where treatments are tailored to each individual’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health data. Robotics will become more autonomous, performing surgeries and medical procedures with greater efficiency and fewer risks.
- AI-powered diagnostics will continue to improve, enabling doctors to diagnose conditions with a level of accuracy that surpasses human capability. Robotic assistants will help manage patient care, from administering medication to offering companionship in long-term care settings.
- While there are challenges ahead in terms of regulations, costs, and integration, the trajectory for AI and robotics in healthcare suggests that these technologies will continue to grow, enhancing both patient outcomes and the efficiency of healthcare systems worldwide.
Also Read:
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence and robotics are driving some of the most significant medical innovations in recent years. From transforming surgery to enhancing diagnostic accuracy and personalizing treatments, these technologies are reshaping the healthcare landscape. They not only promise better patient outcomes but also offer efficiency improvements across the entire healthcare system.
However, as with all new technologies, challenges remain, including data privacy, high costs, and the need for robust ethical frameworks. Despite these challenges, the future of AI and robotics in medicine looks incredibly promising, with the potential to revolutionize how healthcare is delivered and improve the quality of care for millions around the world.
As these technologies continue to evolve, healthcare providers, patients, and policymakers must work together to navigate the complexities and ensure that AI and robotics contribute positively to the future of healthcare.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the main benefits of AI in healthcare?
AI improves the speed and accuracy of diagnostics, assists in personalized medicine, reduces human error, and streamlines administrative tasks in healthcare.
2. How are robotics used in surgery?
Robotics assist surgeons in performing minimally invasive procedures with greater precision, reducing recovery times, and minimizing complications.
3. Can AI replace doctors in diagnosing diseases?
AI can support doctors by analyzing large amounts of data quickly and accurately, but it is unlikely to replace doctors entirely. AI is a tool to aid decision-making, not a substitute for human expertise.
4. Are AI and robotics safe for patients?
When properly implemented, AI and robotics are generally safe and effective. However, the integration of these technologies must be regulated to ensure safety and effectiveness.
5. What challenges exist in adopting AI and robotics in healthcare?
Challenges include high costs, data privacy concerns, ethical considerations, regulatory issues, and the integration of new technologies into existing systems.
6. How can AI improve drug discovery?
AI can analyze large datasets to identify potential drug candidates more efficiently, accelerating the discovery process and reducing costs.
7. What is the future of AI and robotics in healthcare?
The future of AI and robotics in healthcare involves increasingly sophisticated diagnostic tools, robotic surgeries, personalized treatments, and AI-powered administrative automation.

